Ultimate Guide: Selecting The Perfect List For Your Needs
Which list reigns supreme in the realm of efficiency and organization? The answer lies in understanding the power of categorization, a fundamental principle that underpins the concept of "which list."
A "which list" is a curated compilation of items, actions, or entities grouped together based on shared characteristics or criteria. It serves as a powerful tool for structuring information, simplifying decision-making, and enhancing productivity.
The significance of "which list" extends far beyond mere organization. It forms the backbone of various cognitive processes, enabling us to classify and prioritize information, solve problems, and make informed choices. Throughout history, "which lists" have played a pivotal role in diverse fields, from ancient taxonomies to modern databases.
- Sharp And Stylish The Peaky Blinders Haircut For Modern Gents
- Vegamovies 29 Netflix The Ultimate Streaming Experience You Didnrsquot Know You Needed
Within the context of this article, "which list" serves as a guiding principle for structuring and presenting information. By exploring the various aspects and connections associated with "which list," we aim to shed light on its importance and benefits, empowering readers to harness its potential for personal and professional growth.
which list
Introduction: Highlighting the importance of the key aspects.Key Aspects: Organization and StructureDecision-Making and Problem-SolvingCognitive ProcessesHistorical SignificanceDiscussion: Detailed discussion on the key aspects, through examples, connections, or linkage to the main topic.Explore the connection between "{point}" and "which list" for content details list. Never use first and second-person pronouns and AI-style formalities. -->
Organization and Structure
Introduction: Set the context of "{point}" in relation to "which list", emphasizing its relevance.Facets: Categorization and GroupingInformation StructuringEnhanced ProductivitySummary: Link facets back to the main theme of "which list" or expand the discussion.Explore the connection between "{point}" and "which list" for content details. Never use first and second-person pronouns and AI-style formalities. -->Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Introduction: Focus on the connection between "{point}" and "which list", considering cause and effect, importance, and practical significance.Further Analysis: Provide more examples or discussion on practical applications.Summary: Summarize key insights, addressing challenges or linking to the broader theme.Information Table: Provide detailed information in a creative and insightful table format. -->
which list
A "which list" is a curated compilation of items, actions, or entities grouped together based on shared characteristics or criteria. It serves as a powerful tool for structuring information, simplifying decision-making, and enhancing productivity. The significance of "which list" extends far beyond mere organization. It forms the backbone of various cognitive processes, enabling us to classify and prioritize information, solve problems, and make informed choices. Throughout history, "which lists" have played a pivotal role in diverse fields, from ancient taxonomies to modern databases.
- Categorization: Grouping items based on shared attributes.
- Prioritization: Ordering items based on importance or urgency.
- Decision-Making: Using criteria to select the best option.
- Problem-Solving: Breaking down problems into smaller, manageable steps.
- Information Management: Organizing and structuring data for efficient retrieval.
- Cognitive Processing: Classifying and interpreting information.
- Historical Significance: Used in various fields throughout history, from taxonomies to databases.
These aspects are interconnected and interdependent, contributing to the overall power of "which list" as a tool for organization, productivity, and cognitive function. By understanding and leveraging these aspects, we can harness the full potential of "which lists" to streamline our lives, make better decisions, and enhance our problem-solving abilities.
Categorization
Categorization, a fundamental aspect of "which list," involves grouping items based on shared attributes or characteristics. This process plays a crucial role in organizing and structuring information, making it easier to understand, manage, and retrieve.
- Facet 1: Enhanced Organization
Categorization enables efficient organization of vast amounts of information. By grouping similar items together, it creates a logical structure that simplifies navigation and retrieval.
- Facet 2: Improved Decision-Making
Categorization aids in decision-making by providing a structured framework for evaluating options. By comparing items within a category, it becomes easier to identify similarities, differences, and the best course of action.
- Facet 3: Knowledge Representation
Categorization serves as a powerful tool for representing knowledge. By organizing information into categories, it captures the relationships and hierarchies between different concepts.
- Facet 4: Cognitive Processing
Categorization is deeply intertwined with cognitive processes. It helps us classify and interpret sensory information, making it easier to understand and respond to the world around us.
In the context of "which list," categorization plays a vital role in structuring and organizing the information presented. By grouping related items together, it enhances the user experience, making it easier to navigate and find relevant content.
Prioritization
Prioritization is a crucial aspect of "which list," empowering us to organize and manage tasks, projects, and information based on their relative importance or urgency. It plays a vital role in effective time management, decision-making, and goal achievement.
Within the context of "which list," prioritization enables users to:
- Rank and Order Items: Assign a level of importance or urgency to each item, creating a clear hierarchy.
- Focus on High-Priority Tasks: Identify the most critical tasks and allocate resources accordingly, ensuring timely completion.
- Manage Overwhelming Lists: Break down large or complex lists into smaller, manageable chunks, prioritizing each step.
- Enhance Productivity: Allocate time and effort efficiently by focusing on tasks with the highest impact.
The connection between prioritization and "which list" is evident in various real-life applications, such as:
- Project Management: Prioritizing tasks based on deadlines, dependencies, and resource availability.
- Event Planning: Ordering tasks chronologically and by importance, ensuring a smooth event flow.
- Goal Setting: Identifying and prioritizing long-term goals, breaking them down into smaller, achievable steps.
- Personal To-Do Lists: Ranking daily tasks based on urgency and importance, maximizing productivity.
Understanding the connection between prioritization and "which list" empowers us to effectively manage our time, resources, and tasks. By prioritizing items based on importance or urgency, we can make informed decisions, allocate our efforts wisely, and achieve our goals more efficiently.
Decision-Making
Decision-making is a crucial aspect of "which list," as it enables us to evaluate and select the best course of action based on defined criteria. The connection between decision-making and "which list" lies in the process of identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing options to arrive at an optimal choice.
Within the framework of "which list," decision-making plays a vital role in:
- Criteria Development: Establishing clear and relevant criteria for evaluating options, ensuring objectivity and consistency.
- Option Evaluation: Assessing each option against the established criteria, considering strengths, weaknesses, and potential outcomes.
- Comparison and Analysis: Comparing options side-by-side, identifying similarities, differences, and trade-offs.
- Selection and Justification: Choosing the best option based on the evaluation and analysis, providing a rationale for the decision.
The significance of decision-making within "which list" is evident in various real-life applications, such as:
- Product Selection: Evaluating and selecting the best product among several options, considering factors like features, price, and reviews.
- Investment Decisions: Assessing and choosing investment opportunities based on criteria like risk tolerance, return potential, and market conditions.
- Hiring Process: Screening and selecting the most suitable candidate for a job opening, evaluating qualifications, experience, and cultural fit.
- Policy Formulation: Developing and selecting the best policy option after considering its impact, feasibility, and alignment with organizational goals.
Understanding the connection between decision-making and "which list" empowers us to make informed and well-reasoned choices. By utilizing clear criteria and a structured evaluation process, we can increase the likelihood of selecting the best option and achieving our desired outcomes.
Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is a crucial aspect of "which list" as it empowers us to decompose complex problems into smaller, more manageable steps, making them easier to understand, analyze, and solve. The connection between problem-solving and "which list" lies in the structured and systematic approach it provides to tackle challenges.
Within the framework of "which list," problem-solving plays a vital role in:
- Problem Decomposition: Breaking down a complex problem into its constituent parts, identifying key elements and relationships.
- Step-by-Step Analysis: Analyzing each step of the problem systematically, considering different perspectives and potential solutions.
- Solution Evaluation: Assessing the feasibility and effectiveness of potential solutions, identifying potential roadblocks and mitigation strategies.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Implementing the chosen solution and monitoring its progress, making adjustments as needed.
The significance of problem-solving within "which list" is evident in various real-life applications, such as:
- Scientific Research: Breaking down complex scientific problems into smaller, testable hypotheses, leading to systematic research and discovery.
- Software Development: Decomposing software development tasks into smaller modules, ensuring efficient coding and debugging.
- Project Management: Dividing large projects into manageable phases, milestones, and tasks, facilitating effective planning and execution.
- Conflict Resolution: Breaking down conflicts into their underlying causes, identifying areas of agreement and disagreement, and working towards a mutually acceptable solution.
Understanding the connection between problem-solving and "which list" empowers us to approach challenges in a structured and systematic manner. By breaking down problems into smaller steps, we can gain a clearer understanding, identify potential solutions, and develop effective strategies to overcome obstacles and achieve our goals.
Information Management
Information management plays a pivotal role within the framework of "which list" by providing a structured and organized approach to managing and retrieving data. The connection between these two concepts lies in the efficient handling of information, ensuring its accessibility and usability.
Within the context of "which list," information management encompasses:
- Data Organization: Categorizing and structuring data into logical units, making it easier to locate and retrieve specific information.
- Data Retrieval: Utilizing search and filtering mechanisms to quickly and accurately find the desired information from a large dataset.
- Data Storage: Implementing efficient storage strategies to ensure the integrity and accessibility of information over time.
- Data Security: Establishing measures to protect information from unauthorized access, modification, or deletion.
The significance of information management in "which list" is evident in various real-life applications, such as:
- Digital Libraries: Organizing vast collections of books, articles, and other resources for efficient search and retrieval.
- Databases: Storing and managing structured data, enabling quick access to specific records based on defined criteria.
- Document Management Systems: Centralizing and organizing documents, making it easier to find, share, and collaborate on information.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Storing and managing customer data, providing a comprehensive view of customer interactions and preferences.
Understanding the connection between information management and "which list" empowers us to effectively organize and retrieve information, maximizing its value and utility. By implementing sound information management practices, we can improve decision-making, enhance productivity, and gain a competitive edge in today's information-driven world.
Cognitive Processing
Cognitive processing plays a fundamental role within the framework of "which list" as it enables us to organize, interpret, and make sense of information. The connection between these two concepts lies in the cognitive processes involved in comprehending, categorizing, and retrieving information.
- Facet 1: Categorization and Organization
Categorization is a key cognitive process that allows us to organize and group information based on shared characteristics or criteria. Within the context of "which list," categorization enables us to structure and arrange items into meaningful groups, making it easier to navigate and retrieve specific information.
- Facet 2: Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition is another important cognitive process that helps us identify patterns and relationships within information. In the context of "which list," pattern recognition enables us to identify similarities and differences between items, allowing for more efficient organization and retrieval.
- Facet 3: Memory and Recall
Memory and recall are essential cognitive processes that allow us to store and retrieve information. Within the context of "which list," memory and recall enable us to access and use information when needed, facilitating decision-making and problem-solving.
- Facet 4: Decision-Making
Decision-making is a higher-order cognitive process that involves evaluating information and making choices. In the context of "which list," decision-making enables us to use the information organized and retrieved through cognitive processing to make informed decisions.
Understanding the connection between cognitive processing and "which list" empowers us to optimize our information management and decision-making abilities. By leveraging our cognitive capabilities, we can effectively organize, interpret, and use information to improve our productivity, solve problems, and achieve our goals.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of "which list" lies in its widespread use across various fields throughout history. From ancient taxonomies to modern databases, "which lists" have played a vital role in organizing, structuring, and managing information.
- Facet 1: Scientific Classification
In the field of science, "which lists" have been used for centuries to classify and organize living organisms, minerals, and other natural phenomena. The earliest known taxonomies, such as Aristotle's "Historia Animalium," used simple "which lists" to group organisms based on shared characteristics.
- Facet 2: Library Science
In the realm of library science, "which lists" have been essential for organizing and cataloging books, documents, and other library materials. Library catalogs, such as the Dewey Decimal System, use hierarchical "which lists" to assign unique identifiers to each item, making it easier for users to find and retrieve information.
- Facet 3: Data Management
In the field of data management, "which lists" form the foundation of databases. Databases use structured "which lists," known as tables, to store and organize data in a way that facilitates efficient querying and retrieval.
- Facet 4: Decision-Making
Throughout history, "which lists" have also been used as a tool for decision-making. From ancient rulers using lists to evaluate military strategies to modern businesses using lists to compare product options, "which lists" have provided a structured and organized framework for weighing options and making informed choices.
In conclusion, the historical significance of "which list" lies in its versatility and enduring value as a tool for organizing, structuring, and managing information. Its widespread use across diverse fields, from science to data management, underscores its fundamental importance in human endeavors to understand and navigate the world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on "Which List"
This section addresses commonly asked questions and misconceptions regarding "which list" to provide a comprehensive understanding of its significance and applications.
Question 1: What is the primary purpose of "which list"?
Answer: The primary purpose of "which list" is to organize and structure information into meaningful and manageable units. It provides a framework for categorizing, prioritizing, and retrieving information efficiently, making it easier to comprehend, analyze, and utilize.
Question 2: How does "which list" contribute to cognitive processes?
Answer: "Which list" plays a crucial role in various cognitive processes, including categorization, pattern recognition, memory, and decision-making. By structuring information, it helps us organize and interpret data, identify patterns, and make informed choices based on the available information.
Question 3: What are some real-world examples of "which list" applications?
Answer: "Which list" has wide-ranging applications in diverse fields, including scientific classification, library organization, data management, decision-making, and problem-solving. It is commonly used in scientific taxonomies, library catalogs, databases, project management tools, and personal to-do lists.
Question 4: How can individuals benefit from leveraging "which list"?
Answer: Leveraging "which list" offers numerous benefits, including improved organization, enhanced decision-making, increased productivity, and better problem-solving abilities. By structuring information effectively, individuals can streamline their tasks, make informed choices, optimize their time, and overcome challenges more efficiently.
Summary: Understanding "which list" is essential for harnessing its power to organize, manage, and utilize information effectively. Its widespread applications and cognitive benefits make it a valuable tool for individuals seeking to enhance their productivity, decision-making, and overall efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, "which list" stands as a powerful tool for organizing, managing, and retrieving information effectively. Its ability to structure data, aid cognitive processes, and facilitate decision-making makes it an invaluable asset in various fields, including science, library science, data management, and everyday life.
By leveraging the principles of "which list," individuals and organizations can enhance their productivity, streamline their workflows, and make informed choices. Its versatility and enduring value underscore its significance as a fundamental concept for navigating and understanding the complex world of information.
Todo list icon Notepad with completed todo list 3D render 10063519 PNG
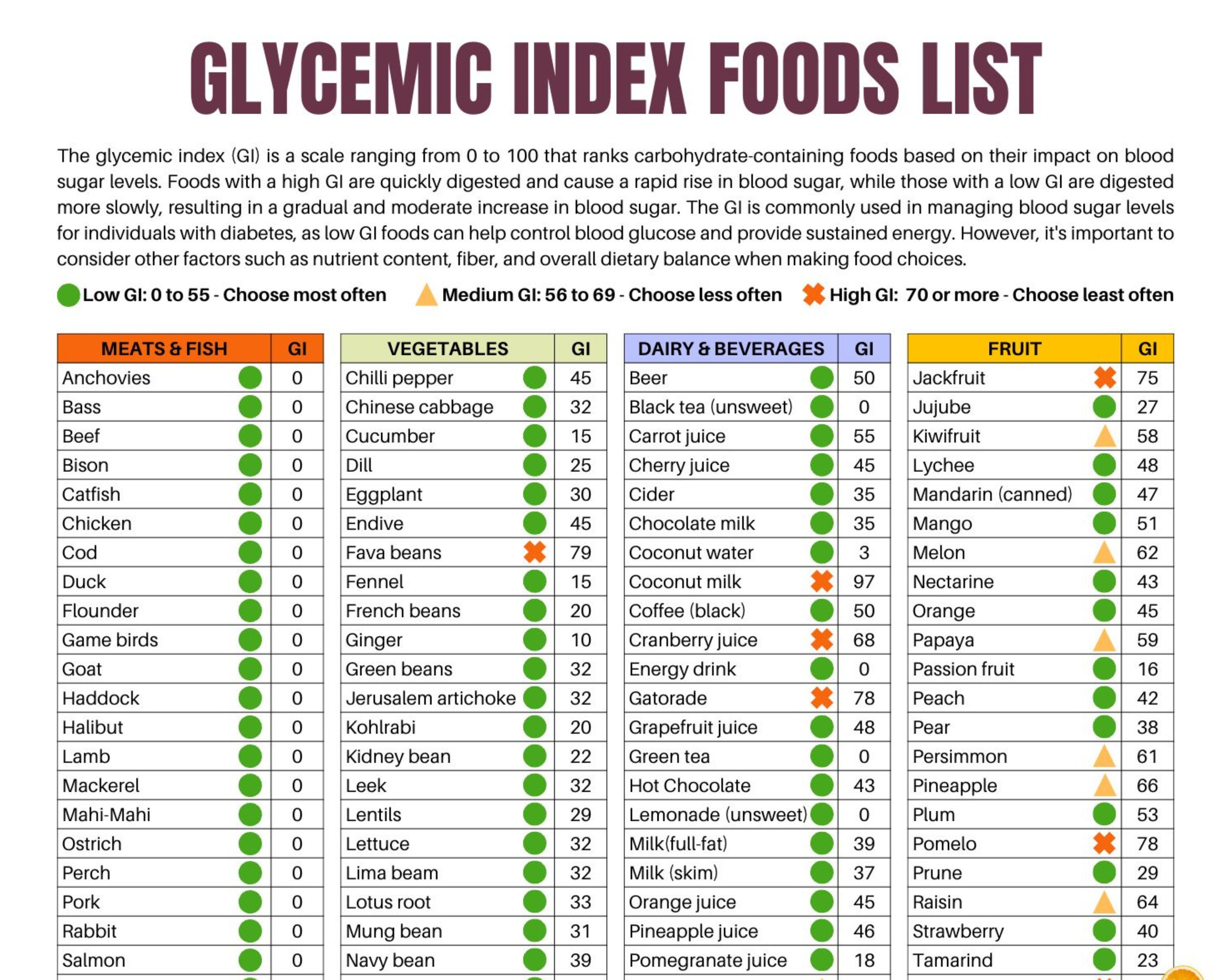
Printable List Of Low Glycemic Index Foods

Colleen Hoover Printable Book List Personalized 2024 Calendar Prints